
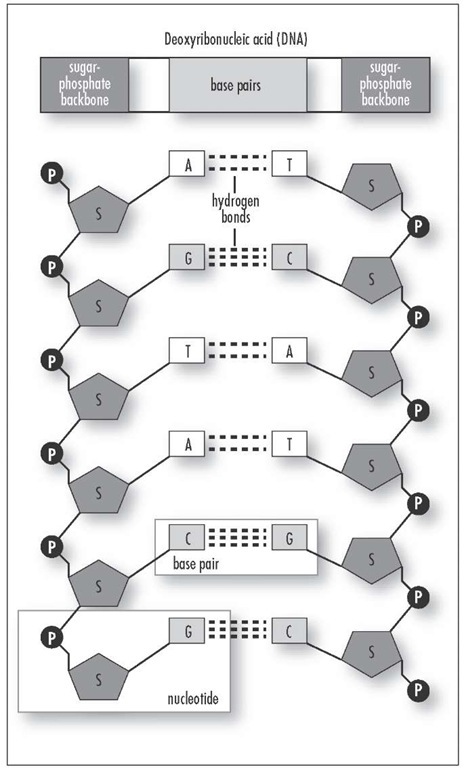
Your DNA could stretch from the Earth to the Sun and back about 600 times.Nucleotides join together to form strands of RNA or DNA that carry and convey information that codes for the sequence of amino acids in proteins and defines features like our eye colour.On the early Earth, nucleotides could have been formed from hydrogen cyanide, when exposed to UV radiation and combined with hydrogen sulfide and phosphate.In our cells, a wide variety of proteins are needed to assemble water-insoluble lipids from simple, water-soluble precursors such as acetic acid and phosphate-containing molecules.An intermediate molecule on the route to production of lipids is glycerol, which is widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and to make longer-lasting soap bubbles.Many vitamins, including vitamin A and D, are fat-soluble, meaning that they must be associated with fat/lipid molecules in order to be absorbed by our body.Lipids combine into membrane bubbles that form the edge of our cells as well as separated compartments within our cells.On the early Earth, lipids could have been produced upon the exposure of mixtures of simple molecules, such as hydrogen cyanide, hydrogen sulfide, and phosphate to sunlight and heat.In our cells, amino acids can be acquired from protein in our diet or built from other nutrients.The human body has about 100,000 different types of proteins, performing a huge number of different functions.Amino acids are used to make proteins by reacting them together in a long chain.On the early Earth, amino acids could have formed from hydrogen cyanide, water, and ammonia, using sunlight as an energy source.But how each of these is made in modern biology is very different to how they were made at the emergence of life.

Each is used by our cells to make more complex molecules and structures necessary for life. Three important building blocks are amino acids, lipids, and nucleotides.
Simple molecules about to react together to produce nucleotides The simple molecules found on the early Earth were capable of reacting together in different ways to produce the building blocks of life.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
